Plugs
Everyone is familiar with the plugs and sockets we see and use every day in our lives. But have you heard of industrial plugs and do you know anything about them?
If not, you should hardly be surprised or think you don’t know enough. They are specifically for industry and it is quite normal for ordinary people not to be familiar with them.
Whether you have come across this page while searching for similar plug connections or just out of curiosity, we will give you a more detailed overview of industrial plugs and sockets, their uses in industry and everything you need to know about them.
What are plugs and sockets?
Let's start with the basics to acquaint you in full with these plugs. Interestingly, the Bulgarian word for a plug (shtepsel) comes from the German word "stöpsel."
Plugs are generally used to draw electrical power. Conversely, plug boxes, commonly known as sockets, are electrical power outlets.
By combining the two, we can create an electrical circuit that powers all our everyday electrical appliances, without which we can hardly imagine modern life.
They have the same use in industry, but with different power, voltage and current ratings.
What is the difference between an ordinary plug and an industrial plug?
To clarify the difference between an ordinary and an industrial plug, we need to digress briefly and explain the difference between a single-phase and a three-phase electric power supply.
The difference between single-phase and three-phase power supplies lies in the voltage in the wiring of each plug and socket.
We are all familiar with single-phase electricity because we use it in our homes. It consists of three insulated conductors. The current flows through two active conductors and one neutral.
Electricity at 120 volts flows through each of the active conductors, while the neutral conductor is disconnected from the transformer.
Three-phase power supplies, as you may have guessed, are those widely used in industry. A three-phase power supply can handle more voltage in the electrical circuit and is therefore better suited for powering large machines and installations, but also differs in the following ways form a single-phase power supply:
A three-phase power supply has four conductors. Three of them run electric current at 120 volts, while the fourth is neutral. The four conductors are differently colour-coded: the three conductors through which electric current passes are black, red and blue, while the neutral conductor is white. There is also another wire to the entire installation, which is green in colour and is used for earthing.
The following example illustrates the above: A single-phase power supply could be compared with someone pushing a trolley up a steep hill. A three-phase power supply, on the other hand, can be likened to three people of equal strength pushing the trolley up the hill.
Perhaps you now understand the differences between a single-phase and a three-phase power supply, and why the latter is better suited to industrial needs, while the former is mainly used for domestic needs.
Now that we have clarified the differences between a single phase and a three phase power supply, here are the differences between an ordinary plug and an industrial plug.
Firstly, industrial plugs have more than the two contact pins found in most ordinary plugs. This is to increase electrical conductivity. Note that plugs used in Bulgaria and the European Union are standard with two contact pins, but in other countries such as the United States or Brazil, domestic plugs have three pins. Accordingly, in Bulgaria, plugs with more than two contact pins are considered as industrial.
Secondly, industrial plugs are made of much better materials, as they are used at a much higher voltage.
The third difference is the price. This makes perfect sense: industrial plugs are much more expensive than their domestic analogue.
What industrial plugs are used for and in what sectors
As described above, industrial plugs are mainly used for industrial purposes. We will now introduce you a little more to this topic.
Plugs and sockets of this type can be used for both outdoor and indoor consumers. They are used in a large and varied number of sectors including:
- Manufacturing;
- Agriculture;
- Chemical industry;
- Agri-food sector;
- Air transport sector;
- Ports;
- Ships;
- Metal industry;
- Power Plants;
- Construction;
- Entertainment;
- Automation;
- Packaging;
- Air conditioners;
- Nuclear power plants;
- Transport;
- and may more.
The different industrial plugs are designed to meet the variable requirements of the consumables used.
Advantages of industrial plugs
Compared to domestic plugs and contacts, industrial plugs have several main advantages.
The colours of industrial plugs and sockets correspond strictly to their voltage rating. For example, blue plugs are rated for 200 volts, while red plugs carry 380 volts. Knowing this, your choice will be much easier.
Another major advantage is the electric shockproof design of industrial plugs. This is achieved by means of the earth pin, which is longer than the phase and neutral pins of the plug. This means that in all cases the consumer will be earthed before an electric shock can occur.
Another advantage we should emphasise is the high level of safety. Industrial plugs and sockets are very well protected to protect people from electric shocks when they touch any part.
The service life of industrial plugs is also much longer than that of their domestic counterpart. While domestic plugs have a service life of about 4500-5000 insertions, industrial plugs operate on average for about 10 years, or almost 100,000 insertions.
How to choose an industrial plug
When choosing an industrial plug or socket, you should be aware of a number of features before making a final purchase.
Look through the different types of industrial plugs and consult a professional about what plugs you need.
Take the requirements of the surroundings into account: if the industrial plug is used in corrosive, humid or high temperature environments, you will need a higher grade product with a higher protection level.
It is important to investigate the requirements of your machines/appliances. Each consumer has its own power, voltage and other ratings. If the industrial plug or socket does not meet these requirements, they may damage the consumer.
-
To the product
 ELMARK PLUG WITH SWITCH 16А 2Р+Е LIGHTED WHITE 192127/WH
ELMARK PLUG WITH SWITCH 16А 2Р+Е LIGHTED WHITE 192127/WHType Plug Rated current 16 A Number of poles 2 Colour White -
-
To the product
 ELMARK SCHUKO PLUG 10A 2P WHITE 192130/WH
ELMARK SCHUKO PLUG 10A 2P WHITE 192130/WHType Plug Rated current 10 A Number of poles 2 Colour White -
-
To the product
 ELMARK SCHUKO PLUG WITH RING 16А 2Р+Е BLACK 192132/BL
ELMARK SCHUKO PLUG WITH RING 16А 2Р+Е BLACK 192132/BLType Plug Rated current 16 A Number of poles 2 Colour Black -
-
To the product
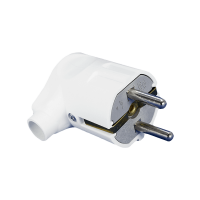 ELMARK ANGLE SCHUKO PLUG 16А 2Р+Е WHITE 192129/WH
ELMARK ANGLE SCHUKO PLUG 16А 2Р+Е WHITE 192129/WHType Plug Rated current 16 A Number of poles 2 Colour White -
-
To the product
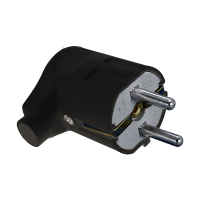 ELMARK ANGLE SCHUKO PLUG 16А 2Р+Е BLACK 192129/BL
ELMARK ANGLE SCHUKO PLUG 16А 2Р+Е BLACK 192129/BLType Plug Rated current 16 A Number of poles 2 Colour Black -
-
To the product
 POWER CABLE H03VV-F 2G0,50MM? WITH SWITCH 2M BLACK 47007/BL
POWER CABLE H03VV-F 2G0,50MM? WITH SWITCH 2M BLACK 47007/BL-
Brand

-
Brand
-
To the product
 POWER CABLE H03VV-F 2G0,50MM? WITH SWITCH 2M WHITE 47007/WH
POWER CABLE H03VV-F 2G0,50MM? WITH SWITCH 2M WHITE 47007/WH-
Brand

-
Brand
-
To the product

-
To the product

-
To the product

-
To the product

-
To the product

-
To the product

-
To the product

-
To the product

-
To the product

-
To the product

-
To the product

-
To the product

-
To the product

Prices are VAT inclusive