Voltmeters – different types and uses
Everyone has heard the word voltmeter at least once in their life. Although it sounds familiar, not everyone is fully clear about what voltmeters are.
Whether you want to buy a new voltmeter or simply learn more about this device and its benefits, you can find very useful information on Elmark's blog, which will be very useful for you in the future.
We will try to familiarise you below in full with the device called the voltmeter, its functionality, its various types and a little story that we think you will find interesting.
Main functions of a voltmeter
Generally speaking, a voltmeter is an instrument used to measure voltage.
Its other main purpose is to measure the electrical potential difference between two separate points in an electrical circuit. Depending on its type, the voltmeter can measure both DC and AC electricity.
Voltmeters are usually produced in a wide range of styles. Instruments permanently mounted on a panel are usually used for monitoring generators or other fixed appliances.
Portable devices, usually equipped to measure current and resistance in the form of multimeters, are standard test tools used in electrical work and electronics.
How the voltmeter was invented
Like any other invention, the voltmeter has its own history. It is difficult to identify one single inventor of the voltmeter. A number of scientists contributed to the development of this device and the science of electricity and physics in general.
Michael Faraday is one of the pioneers of experiments and discoveries in the electricity industry. He used a galvanometer to measure voltage and current.
Edward Weston is another brilliant scientist who developed some of the best-known voltmeters and ammeters in the early days of the era of electricity.
His 1886 portable ammeter (which subsequently developed into the multimeter known today) set standards that paved the way for the creation of accurate voltmeters.
It is worth mentioning a number of other people who contributed to the development of the voltmeter: Elihu Thompson, William Stanley, Oliver Shallenberger and Irving Langweir.
Different types of voltmeter
There are several basic varieties of voltmeter which to a large extent determine the functionality of the device.
One of the traditional versions of this appliance is the analogue voltmeter. In this case, the voltage is shown by an arrow. Analogue voltmeters are of the electrostatic type, with a removable coil and an iron.
Moving coil voltmeters also come in two types: one has a permanent magnetic field and therefore only works with direct current. This type of appliance consists of a permanent magnet which creates a magnetic field and a coil connected to a soft piece of metal, which rotates around its own vertical axis.
The other type has a dynamo and consists of two coils, one fixed in place while the other rotates. The benefits of moving coil voltmeters include low energy consumption, easy extension for measuring a wide range of values and the fact that the scale is the same.
However, let's go back to the types of analogue voltmeters, particularly the moving iron voltmeter. This type consists of a moving soft iron and fixed coils. The advantages of this voltmeter are its affordable price, the high weight/torque ratio and the fact that it can be used to measure both alternating and direct current.
The electrostatic voltmeter is another basic type of meter. Here the electricity is measured by electrostatics, using the reciprocal repulsion between two charged circuit boards, which in turn deflect an arrow attached to a spring to show the results.
There are major benefits in using an electrostatic voltmeter and in particular we can mention their high sensitivity, allowing much more accurate measurement, their ability to measure even the smallest voltage and their suitability for high voltages, both with direct or alternating current.
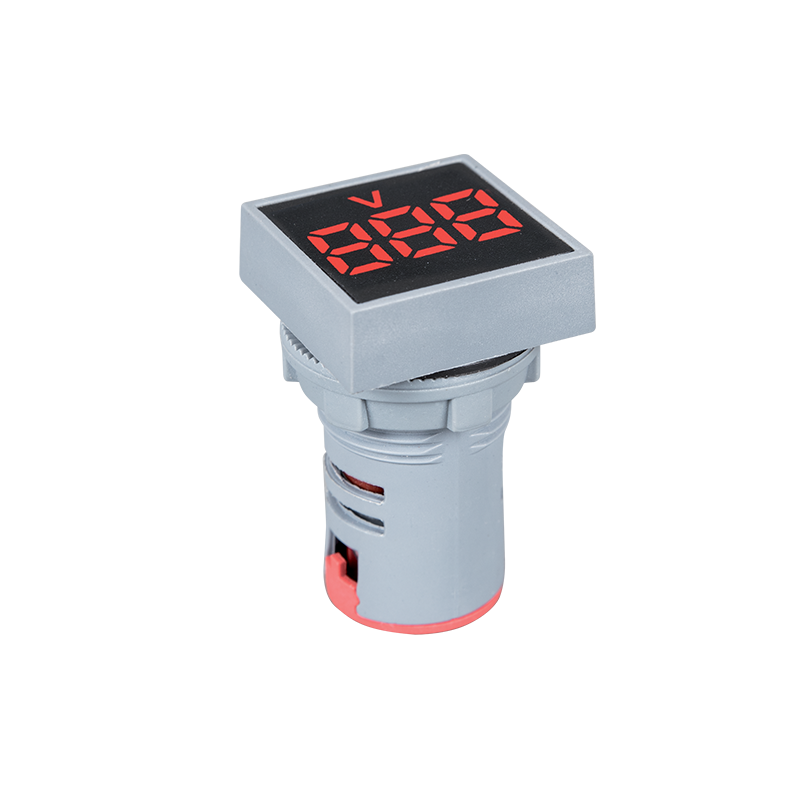
The digital voltmeter is yet another type, used in recent times more than in the past. Apart from the obvious benefits of this type of voltmeter, they are much more modern and well-developed: they reduce parallax errors and have automated polarity, high resolution and precision and automatic variation. All of this was science fiction until recently.
Now that you are more familiar with the different types of voltmeters, you will be much better able to judge which works best for you, depending on the type of current you want to measure.
What are voltmeters used for today?
When electricity first came into use and with the gradual development of electrical science, the voltmeter was used primarily for scientific purposes and much less for domestic and other purposes.
This is no longer the case, mainly because of the stunning development of electricity, the creation of modern electrical appliances without which we can hardly imagine living and the use of electricity practically everywhere around us.
This means that a number of appliances, including voltmeters, can be used for our everyday needs.
Mobile phones, laptops and coffee machines are all appliances that we use every day and which rely on electrical circuits for their power supply. But we should ask ourselves a simple question: do the batteries in our graphics calculator use the same amount of electricity as our coffee machine, for example? The answer is obviously no.
Different circuits require different potential difference values to maintain the electric current. This potential difference is measured with voltmeters.
Why get a voltmeter?
There are many reasons to buy a voltmeter. You may need one without necessarily being a professional electrician or engaged in another trade where electricity plays an essential part.
As you have seen above, there are now many different types of voltmeters with which everyone can measure the voltage and electrical potential of any appliance for themselves.
We at Elmark recommend that everyone should have a voltmeter, or at least a multimeter, which can also measure voltage and other values.
Electricity is a key part of our lives and will probably continue to be in the future. It will probably be very useful for you to learn more about it and be more informed about the electricity we use in our homes. Having a voltmeter will help you greatly in this respect.